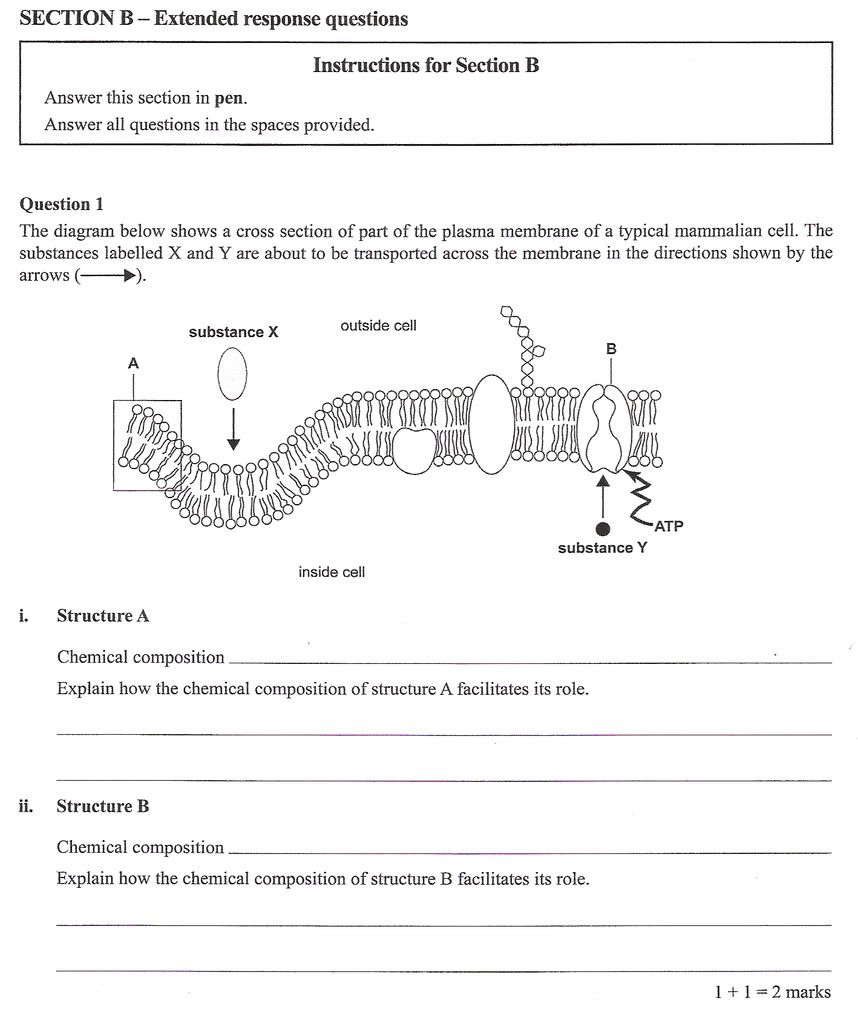
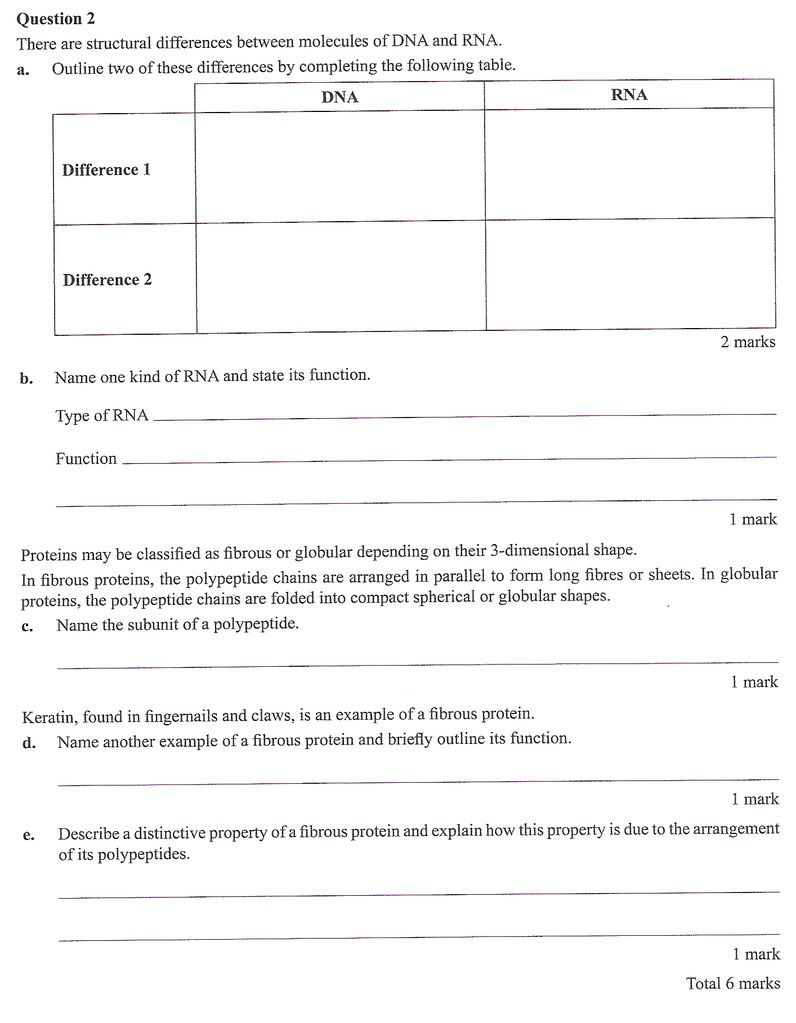
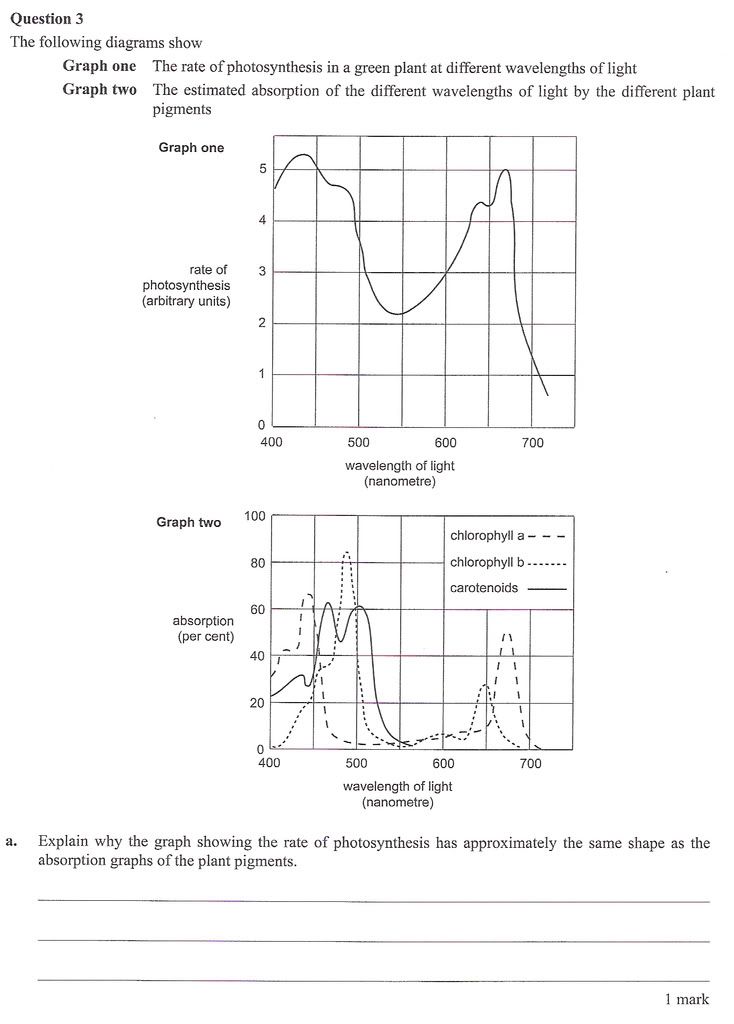
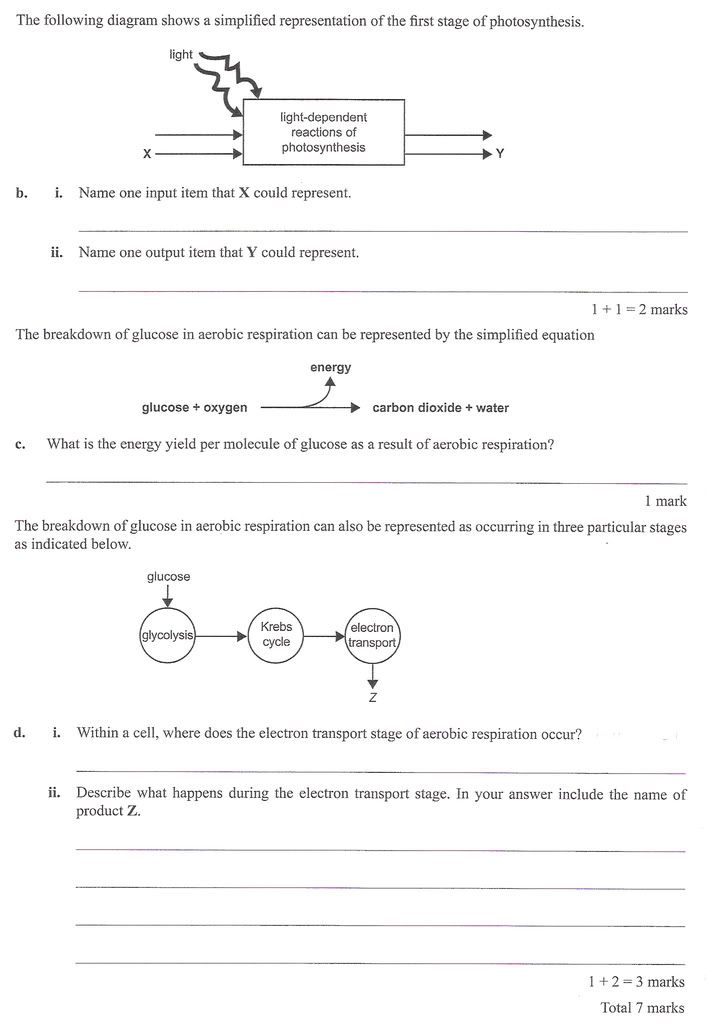
VCE Biology Unit 3 Exam 2008
Section A - Multiple ChoiceConsider the following plant cell.
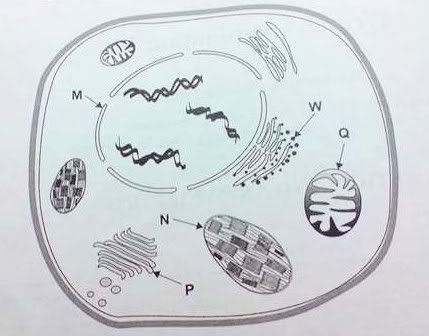
Question 1A process occurring at structure
W in this plant cell would be
A packaging of moleculesB aerobic respirationC protein synthesis
D DNA replicationQuestion 2In this plant cell, the light-dependent reactions of photosynthesis occur in structure
A N
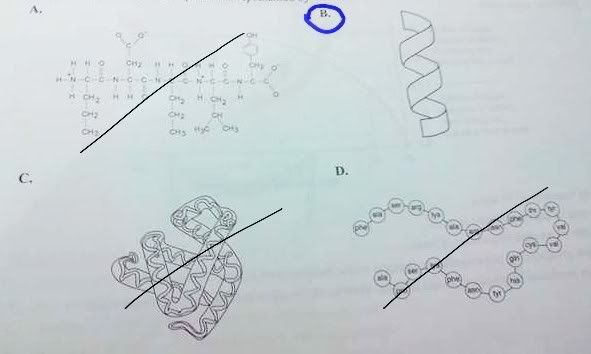
B MC QD PQuestion 3The secondary structure of a protein is represented by
 Question 4
Question 4The four main types of biomacromolecules in a cell are
A monomers, polymers, DNA and RNA
B proteins, carbohydrates, DNA and RNAC nucleic acids, proteins, carbohydrates and lipids
D monosaccharides, disaccharides, polysachharides and proteinsQuestion 5The enzyme maltase catalyses the breakdown of maltose into glucose.
Maltase was added to a tube containing a solution of maltose in water and incubated at 37 degrees Celcius. The amount of glucose produced was monitored over a period of time. No maltose remained in the end.
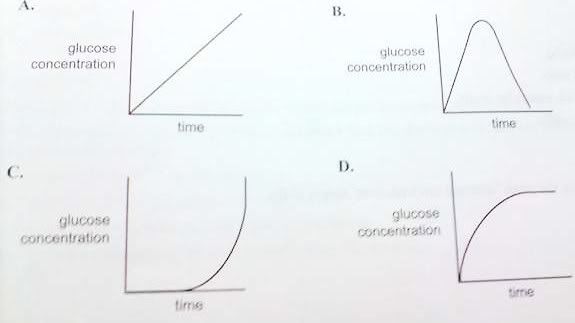
D
Question 6The following graph shows the relationship between light intensity and net oxygen uptake or output by a particular green plant.
At a light intensity of 10 units
A the rate of photosynthesis is zero
B the rate of aerobic respiration is zeroC oxygen produced by photosynthesis is equal to the oxygen sed by aerobic respiration
D oxygen produced by photosynthesis is equal to twice the oxygen used by aerobic respirationQuestion 7Glycogen is
A a polysaccharide found in animal cells
B an energy-storing lipid molecule
C a molecule in which plants store sugars
D a polysaccharide found in plant cell wallsQuestion 8Lipids characteristically
A are hydrophobic
B catalyse reactions
C have low energy content
D are information-storage moleculesQuestion 9The lymphatic system
A controls blood clotting
B contains red blood cells
C has vessels with thick muscular wallsD contains phagocytic cells
Question 10In a multicellular organism, the term 'internal environment refers to the
A cytoplasm
B cell organelles
C nuclear regionsD extracellular fluid
Question 11The following diagram shows a synapse betwee two neurons.
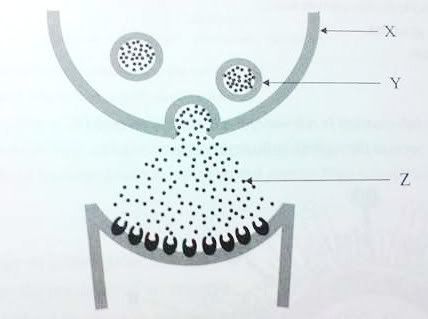
The arrows
X,
Y and
Z point respectively to a
A pre-synaptic terminal, a Golgi body and acetylcholineB pre-synaptic terminal, a vesicle and a neurotransmitter
C post-synaptic terminal, a vauole and a neurotransmitter
D post-synaptic terminal, a mitochondrion and acetylcholineQuestion 12Insulin is a complex protein that is said to have a quaternary structure
This means that insulin
A cannot be denatured
B lacks disulfide bridges
C contains all the known amino acidsD has more than one polypeptide chain
Question 13First-line defences that mammals have against invasion by disease-causing bacteria include
A lysozymes
B interferon
C antibodies
D killer T cellsQuestion 14Diptheria is a disease caused by the bacterium
Corynebacterium dephtheriae.
A six-month old baby boy, whose mother and father both had diptheria as children, will develop active immunity against diptheria if he
A is being breast fed
B receives a blood transfusion from the fatherC receives an injection of dead diptheria bacteria
D receives injection of gamma globulin from the motherQuestion 15Facilitated diffusion is a form of cell transport that
A moves oxygen and carbon dioxide across membranes
B occurs against a concentration gradientC requires specific protein channels
D uses energy supplied by ATP(Questions 16 and 17) The following diagram shows a cross section through an influenza virus.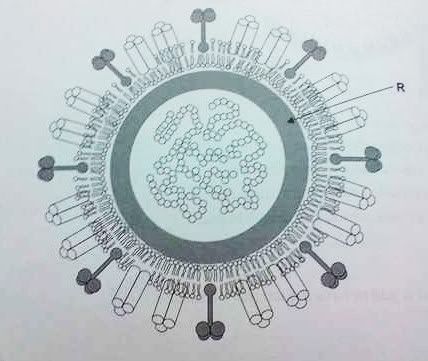 Question 16
Question 16The part of the virus labelled R is its
A antigenic marker
B lipid envelopeC protein coat
D viral genomeQuestion 17A typical characteristic of such a virus is that it
A is destroyed by antibiotics
B releases toxins into the body of the host
C evades detection by the host's immune systemD manipulates the host cell's DNA to procude copies of itself
Question 18Sucrose (cane sugar) is a disaccharide used by plants as a transport molecule. Sucrose is formed in the following reaction
glucose + fructose [enzyme]---> sucrose
With reference to this process it can be stated that
A glucose and fructose are polysaccharidesB the production of sucrose is an endergonic reaction
C sucrose is a reactant and glucose is a product of the reaction
D a molecule of fructose contains more stored energy than a molecule of sucroseQuestion 19Activation energy in a biological reaction
A increases in the prescence of an enzyme
B increases with an increase n temperatureC is the energy required to start the reaction
D is involved in the formation of complex molecules onlyQuestion 20<insert text cbf typing>
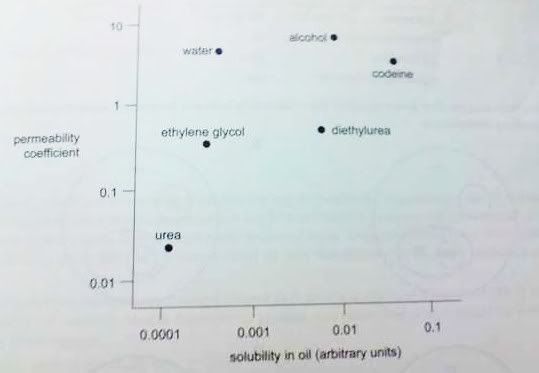
From the graph you can conclude that
A water is more lipid-soluble than alcoholB a cell gets rid of urea more slowly than excess water
C drugs like alcohol and codeine enter cells more slowly than ethylene glycol
D ethyene glycol passes through the plasma membrane more easily than diethylurea
Question 21With regard to the pathogen, we can conclude that
A the person has a deficient immune response
B the virulence of the pathogen increased between the 1st and 2nd exposures
C antibodies are only produced after a second exposure to the pathogenD memory cells for antibodies against the pathogen exist at the time of the second exposure
Question 22<insert pic>
AB
C
DQuestion 23A increased production of PTH results in reduction of vitamin D activationB reduced production of PTH results in increased calcium in faeces
C sustained overproduction of PTH results in strengthed bones
D high levels of blood calcium stimulate release of PTHQuestion 24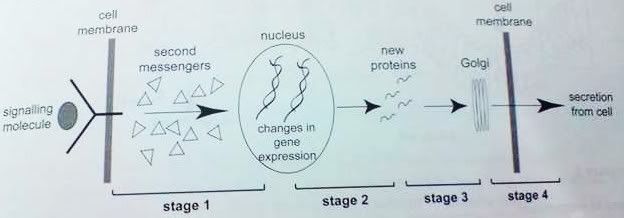
Signal transduction is represented by stage
A 1
B 2
C 3
D 4Question 25<insert huge block of text>
The advice is likely to include directions to
A keep swimming pools free of chlorineB stock any garden pool with fish that eat mosquito larvae
C keep windows and doors open and uncovered to allow airflow
D keep well away from animals that may have been bitten by mosquitoes