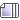
I'm doing some revision of the plasma membrane, and movement across the plasma membrane, and I'd just like to see if my expression for the functions of the components of the plasma membrane are accurate.
Phospholipid Bi-layer:
- The hydrophilic phosphate heads and the hydrophobic fatty acid tails allow the movement of selectively small, uncharged and/or lipid-soluble substances into and out of the cell.
Protein Channel:
- Allow the movement of selective, non-lipid soluble substances into and out of a cell.
Cholestrol - found only in animal plasma membranes:
- Provides more stability and flexibility to the plasma membrane
- Reduces the fluidity of the plasma membrane at normal range temperatures to provide stability to the plasma membrane.
- Increases the fluidity of the plasma membrane