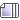
Condensation reaction – forming, synthesis, releases water (The opposite is hydrolysis – adding water to break the bond)Condensation polymerisation is when you have
monomers join together to form a larger thingy called a
polymer.
eg of;
MONOMERS - POLYMERSMonosaccharides - Polysaccharides
Amino acids - Proteins
Nucleotides - Nucleic acids
Alright in that diagram (first one) there is a dumbed down version of a
monomer. It could be anything (i.e. the alpha amino acids in my 2nd diagram).
The monomers have a
-H(hydrogen!) and a
-OH(hydroxide!) coming off it as you can see.
Recall that water is 
. Two hydrogens, one oxygen.
When you join the two monomers. H and OH bond together, then voila, water (

) is released/expelled and a covalent bond is formed between the monomers.
What the first diagram shows now ("3rd" line) is
"monomer-monomer + monomer". A continuation of the process.
If you keep joining monomers together, you get a polymer. In condensation, water is released.
read again if you get it:
2) Polymerization is the process whereby monomers are combined to form polymers, such as amino acids join together to form protein chains. You could draw a more chem based diagram (using your chem knowledge  ) with two monomers and the O-H and H forming H2O, although I doubt that level of knowledge would be required for the biology exam.
) with two monomers and the O-H and H forming H2O, although I doubt that level of knowledge would be required for the biology exam.
2. Annotated diagram: I would draw say an amino acid (NH2-CR-COOH) and another one and then put circles around the OH and H that are reacting, then an arrow, then draw the C-O-N peptide link forming in the middle and the water molecule coming out, all annotated properly
Polymerisation is the process by which polymers are formed, it is known as condensation polymerisation because it produces a water molecule. The opposite is hydrolysis. Your studies on 1/2 chemistry should help you fully understand this element of 3/4 biology
and yes you'll need this for unit 3 chem