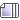
The fatty acids are carboxylic acids with really long carbon chains. The saturated fatty acids do not possess any double bonds within this carbon chain (no C=C double bond, although there is a C=O double bond at the end) and hence possess the maximum number of hydrogen atoms possible.
Glycerol is an alcohol, and we know that when alcohols are mixed with carboxylic acids, they form esters. Since glycerol has three O-H groups, each molecule can engage in condensation reactions with three fatty acids, to form what is known as a triglyceride.
Since we're here using saturated fatty acids (which have the general formula CnH2n+1COOH), we get saturated fats. These are solids at room temperature, as the fatty acids are able to align themselves really closely too each other, due to being straight chains with no double bonds). Unsaturated fats are oils are room temperature, as the double bonds weakens the solidarity of the overall molecule, as it can't pack itself tightly in.
Unlike the unsaturated fatty acids, you can't hydrogenate a saturated fatty acids, or saturated fat.
I feel like I've forgotten something.